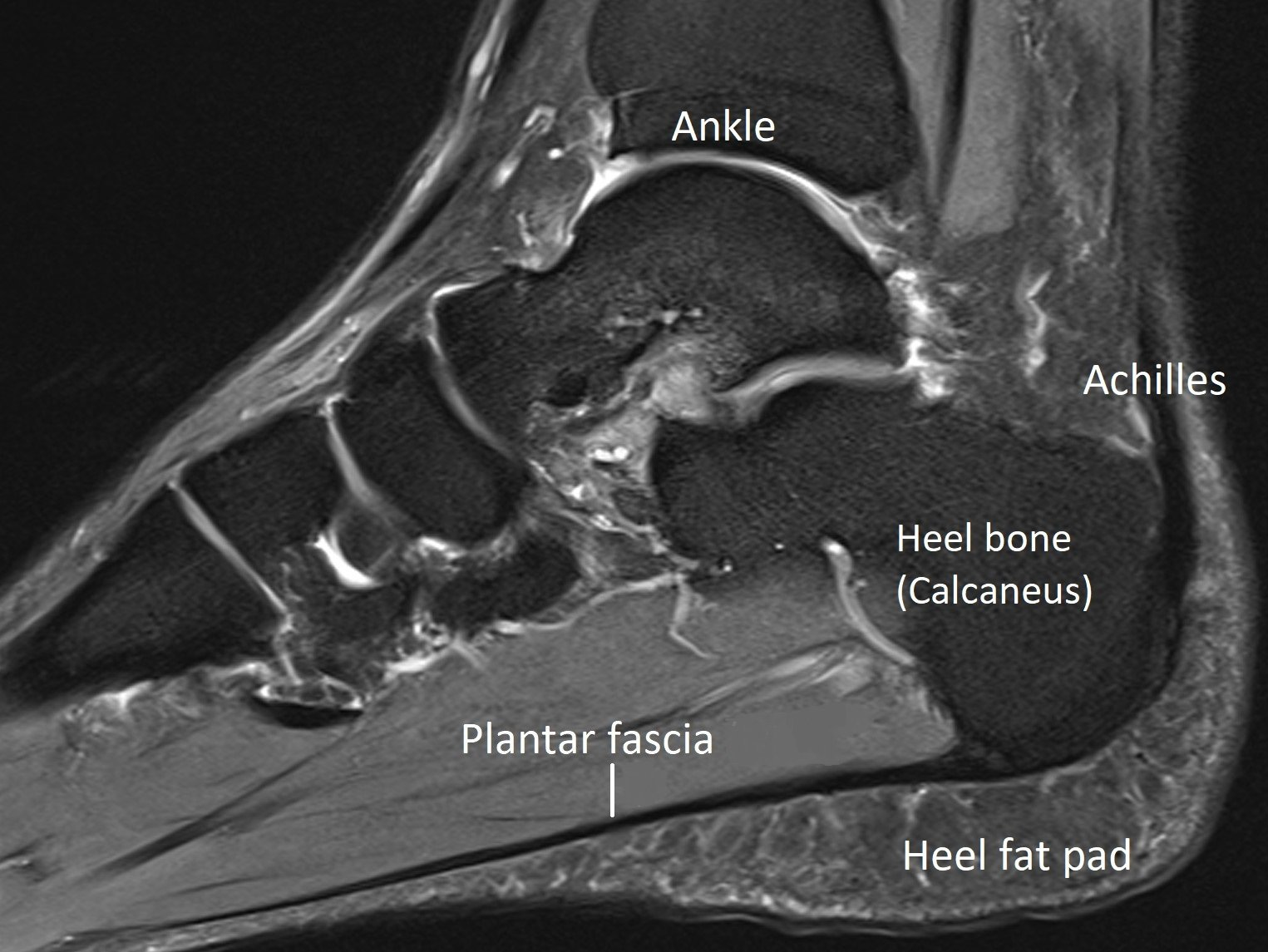
Achilles & Heel - Anatomy and Imaging
- transmit the force of muscle contraction to bone, causing limb movement
- has a complex structure and undergoes repeated loading
- blood supply is not as good as muscle so its healing ability is also not as good.
Plantaris tendon - 90% of people have a very thin tendon running on the inner (medial) side of the Achilles tendon called plantaris. It has no useful function.
Interesting facts: plantaris has the longest tendon in the human body, starting behind the knee and going all the way down to the heel. It is also called the "monkey muscle" as it helps them climb trees.
Paratenon - the Achilles tendon is surrounded by a thin layer of tissue called the paratenon. This allows the tendon to glide smoothly under the skin.
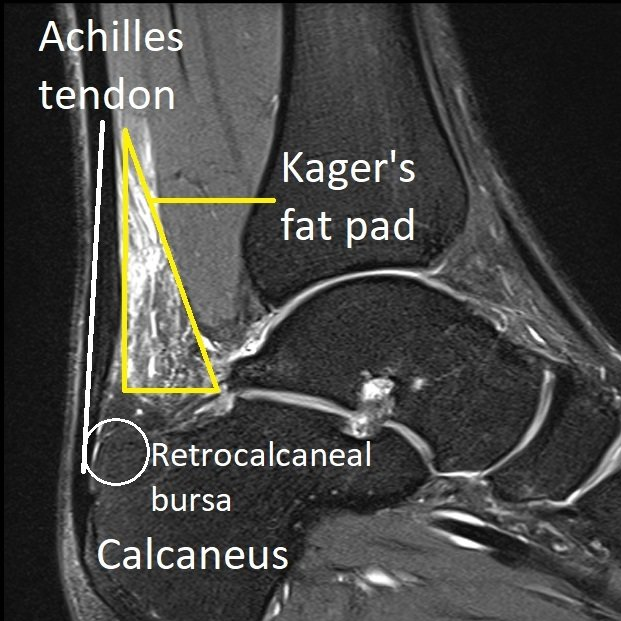
Kager's fat pad - this tissue sits between the paratenon and the muscles at the back of the ankle.
Retrocalcaneal bursa - is a fluid-filled sac located at the back of the heel under the Achilles tendon. It contains lubricating fluid that reduces friction between the tendon and bone.
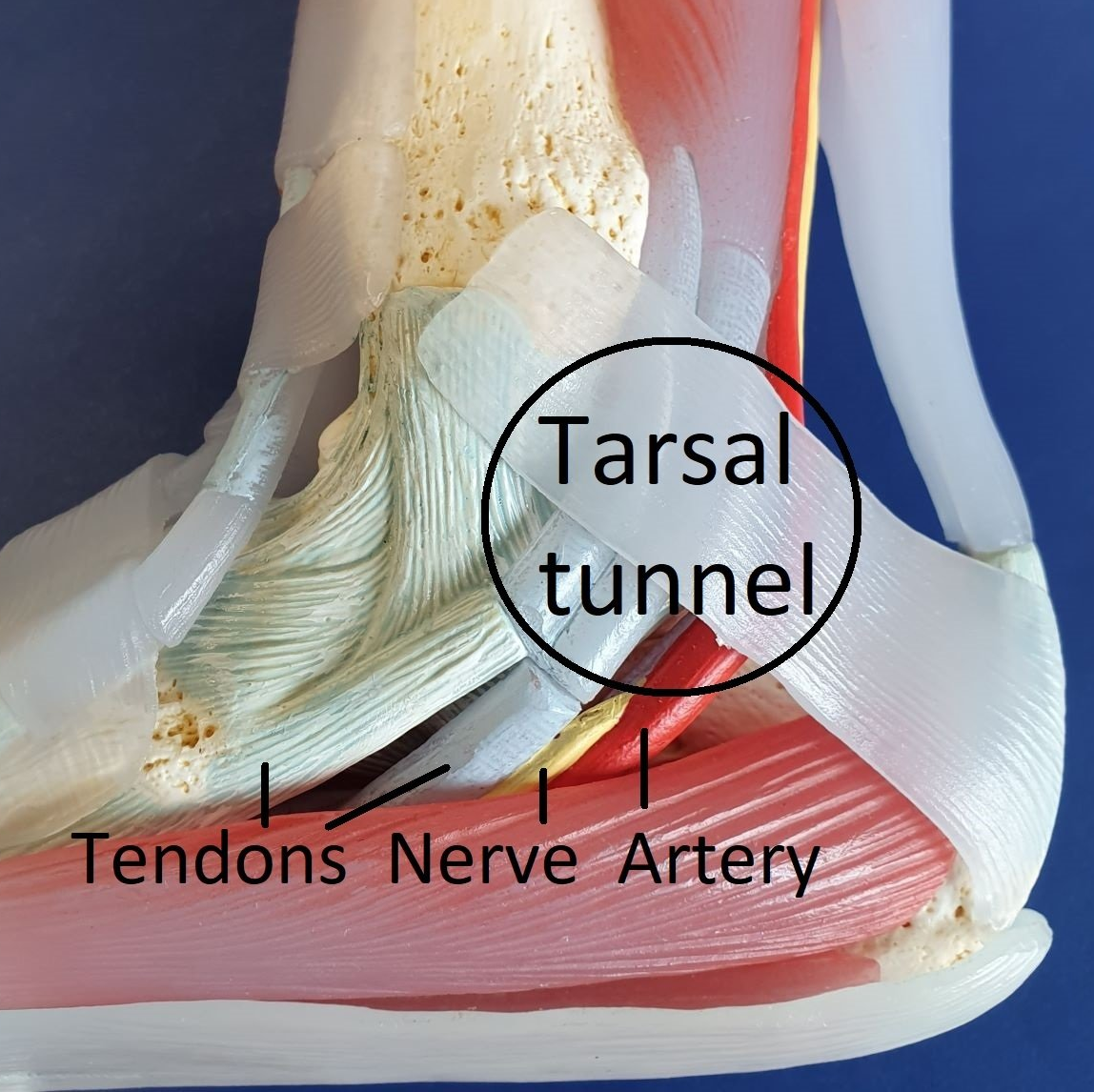
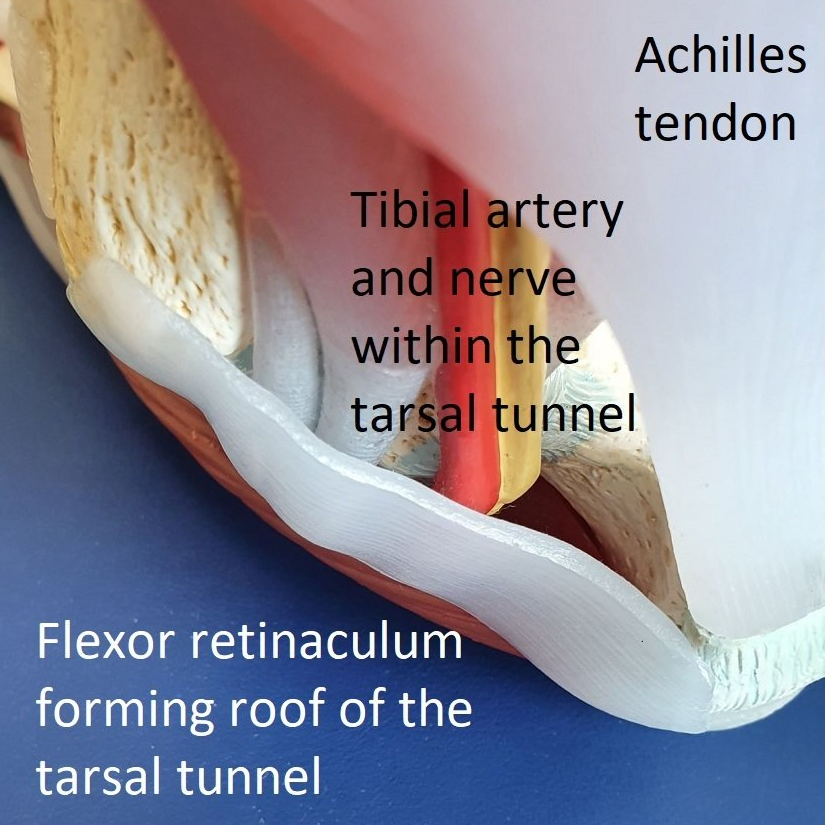
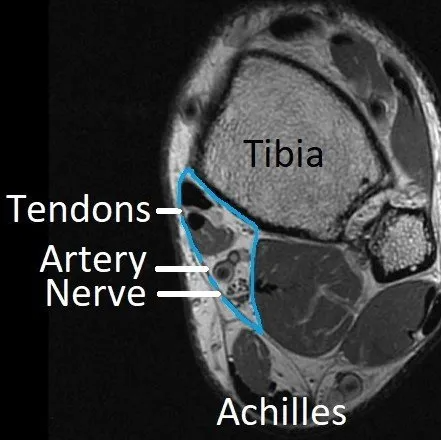
Tarsal tunnel
The tarsal tunnel is a passage from the leg to the foot behind the inner (medial) ankle. Tendons, blood vessels and nerves pass through it (area outlined in blue).